A well-maintained septic system is crucial for ensuring a safe living environment for you and your family. If you’re thinking about replacing or setting up a septic system in New Jersey, or simply want to learn more about its upkeep, it’s vital to grasp its workings. This article provides a comprehensive overview of septic systems, their maintenance, and what to anticipate from a septic system repair service.
We’ll guide you through the signs that might suggest the need for a new septic system, indications that your current system might require replacement, and much more.
Septic systems have been in use for ages, but many homeowners and potential homeowners still have misconceptions about them.
For the longevity of your septic system and to avoid replacements, it’s vital to comprehend its workings and its significance for your well-being and that of your neighbors. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this system and its crucial role in ensuring a safe living environment for your household.
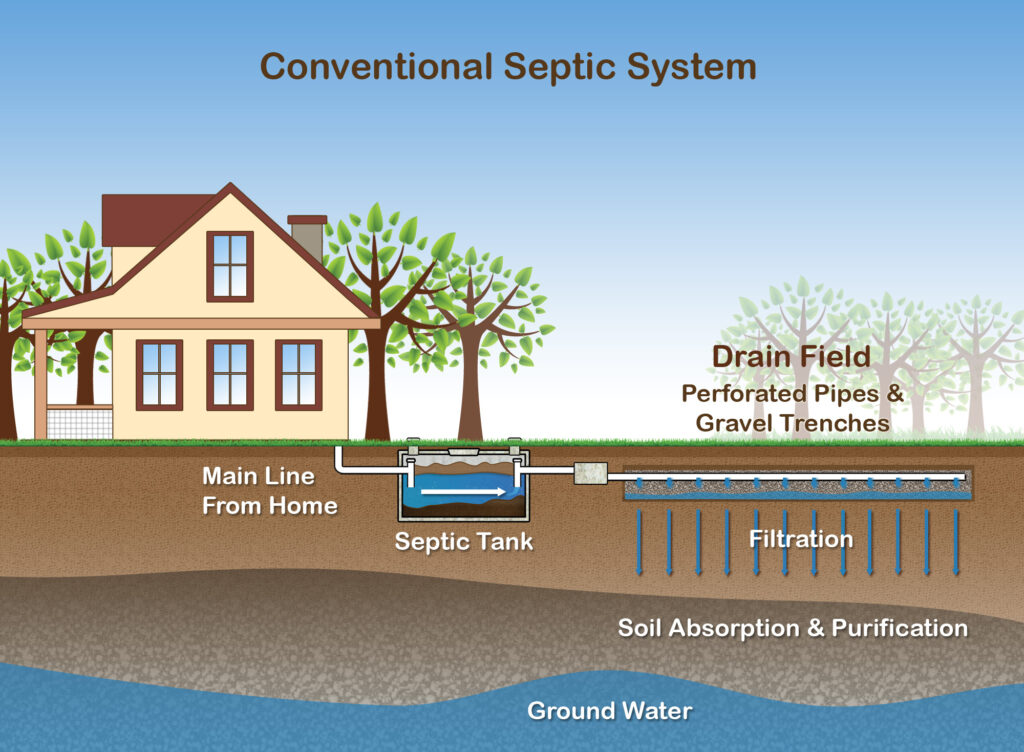
A septic system is responsible for treating and disposing of both liquid and solid wastes. Typically situated partially or wholly below ground, it comprises a tank and a drainfield. Its primary function is to treat the household wastewater that doesn’t enter the public sewer, ensuring it’s purified enough for environmental release without causing harm.
The waste processed by septic systems can be solid or liquid, encompassing gray water (from sinks and showers) and black water (from toilets).
When wastewater enters the septic tank, bacteria work to decompose grease and other organic substances until they’re minute enough to be either percolated into a leach field or absorbed into a drain field. Leach fields distribute the effluent via underground pipes, allowing it to spread into the soil where further bacterial action breaks down the remaining nutrients. On the other hand, absorbent beds use gravel-filled trenches enclosed by impermeable materials like concrete.
The leach field serves a dual purpose: it filters any remaining impurities from the treated water and reintroduces the semi-purified water into the groundwater.
The septic tank itself has three sections: a chamber to hold and settle solid wastes, a clarifying chamber for further liquid waste separation, and a final chamber where the fully treated water is held before discharge.
Ensuring your septic system operates efficiently is fundamental to providing a secure and healthy living space for your family.